Context
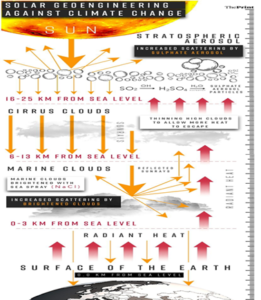
The United States is eyeing a controversial tool to counter global warming: Solar radiation management (SRM), which involves reflecting a small fraction of sunlight into space. What is solar radiation management (SRM)?| Aerosols are tiny particles suspended in a gas form which reduce the heat intensity. |
- SRM aims at injecting the atmosphere with aerosols or using giant mirrors to reflect the sunlight back.
- By reducing the load of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, the SRM is being sold as a futuristic technology that will reduce soaring temperatures in Africa to make it relatively cooler.
- Popular theoretical ideas for SRM include:
- modifying cloud structures
- spraying aerosols into the stratosphere
- ‘Geoengineering’ literally means interventions that change the way the Earth’s systems work.
- Category: Geoengineering is broadly divided into two categories —
- technologies for capturing carbon (carbon dioxide removal)
- methods for managing how much of the Sun’s heat reaches the Earth
- preventing the Sun from heating up the Earth (solar radiation management)
- removing heat from the Earth’s atmosphere into space (Earth radiation management)
Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB)
|
- The call to pursue geoengineering is spurred by the urgency of tackling the fallout of climate change.
- As the world continues to heat, with no end in sight for fossil fuel emissions, solar and other forms of geoengineering are starting to occupy more mainstream space in climate discussions.
- Ideas associated with geoengineering have not been tested or executed yet.
- A draft EU report had flagged the risks associated with geoengineering and called for talks towards an international framework to govern such technologies.
- This is not only dangerous but also frightening and inequitable.
- By dimming the incoming sunlight can upset the anthropogenic equilibrium and, thereby, have a devastating impact by way of:
- disrupting monsoons
- altering cropping patterns
- causing unforeseen problems for the local and regional biodiversity
- extended droughts and incessant rains
Major processes of natural SRM
|
Post Views: 195
