Context:
Role of BRICS Platform:
- India and China recently engaged in a high-level meeting during the 13th BRICS National Security Advisors (NSA) meeting in Johannesburg, South Africa.
| Areas of Discussion | Description |
| China Commitment |
|
| Concerns raised by India |
|
| Other Key Issues Discussed |
|
- BRICS has become an important platform for emerging markets and developing countries to seek strength through solidarity.
- Voice to developing nations: BRICS countries have striven to increase the say and influence of emerging markets and developing countries to constantly inject positive energy into the world of change and disorder, which is the epitome of the capability of BRICS cooperation.
- Three-driver cooperation: BRICS countries’ three-driver cooperation—political and security cooperation, economic cooperation, and people-to-people exchanges—has yielded positive results.
- Congruency in Relationship
- Warmth in Relation: Both countries have jointly advocated the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence.
- Both countries have initiated the “hometown diplomacy”, held two informal summits in Wuhan and Chennai respectively.
- Global Security: Both are working to address regional and global security issues such as terrorism and the spread of weapons of mass destruction.
- Climate Action: Both countries have collaborated on climate change and have both signed on to the Paris Agreement.
- Multilateral Forum: India and China are both members of BRICS, SCO, WTO etc, which reflect common agenda for growth and development
- Cultural Linkages: India and China have a history of cultural exchanges and have established institutions like the Yoga College in China.
- Economies Ties: Bilateral trade has grown significantly, reaching US$100 billion by 2022, with India becoming a large market for project exports from China.
- Warmth in Relation: Both countries have jointly advocated the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence.
- Concern in Relationship:
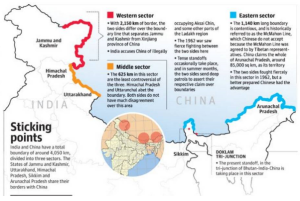
- Border Disputes: Two countries share a 3,500-kilometer border, as well as a shared cultural and religious heritage.

-
-
- However, there have been several instances of conflict and tensions over the last few decades, including the 1962 Sino-Indian War and border clashes that occurred as recently as 2021 and continue to this day.
- Geopolitical Rivals: Both countries are attempting to assert their global influence, and they have competing interests in a number of regions, including the Asia-Pacific and Indian Ocean.
- Water Dispute: The sharing of the Brahmaputra River has been a significant source of tension between India and China.
- China has been constructing numerous dams in the upper reaches of the river on which India has raised objections. However, no formal treaty has been established to address the matter.
- String of Pearls: It is a network of Chinese military and commercial facilities which extend from the Chinese mainland to Port Sudan in the Horn of Africa. India believes this plan, together with the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor and other parts of China’s Belt and Road Initiative as a threat to India’s national security.
- QUAD: The grouping, in terms of International Relations theory, is a product of ‘external balancing’ is seen as a threat by the Chinese government.
- South China Sea: China claims sovereignty over various islands and reefs in the South China Sea as well as its sea lanes of communication and considers them part of its territorial waters.
- Trade Deficit: India’s significant reliance on Chinese imports has resulted in a substantial trade deficit of $100 billion between the two countries.
-
- Sanction of terrorists under UNSC Regime: Listing terrorists and their proxies under the United Nations’ counter-terrorism sanctions regime to address the threat posed by these terror groups and promote global security.
- Solidarity among BRICS nations: To address the challenges brought by the digital age, there is a necessity for unity among BRICS nations to strengthen cyber defenses, promote international cooperation, and establish robust national cyber infrastructure.
- Addressing supply chain disruptions: Supply chain disruptions have had a disproportionate impact on the food security of vulnerable people.
- The issue needs to be urgently addressed which is a shared commitment and common responsibility.
- Cyber Attacks: Cyber-attacks know no borders and the linkage between cyber criminals and terrorists is an emerging concern.
- Regional mechanisms should be utilized to advance common goals and address emerging challenges.
- Respecting Sovereignty of neighbors: Developmental projects such as China’s Belt and Road Initiative should not undermine the sovereignty of the nations.
Post Views: 185
