Context:
NASA detected a signal from its Voyager 2 spacecraft on August 1, after losing communication for over a week.
About Voyager Mission:
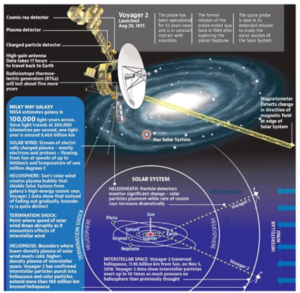 Key features of the Voyager Mission:
Key features of the Voyager Mission:
News Source: The Indian Express
- It is a space exploration program conducted by NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) that launched two spacecraft, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, in 1977.
- Voyager 1: Sept 5, 1977
- Voyager 2: August 20, 1977
- Objective: To study the outer planets of our solar system, including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
 Key features of the Voyager Mission:
Key features of the Voyager Mission:
- Exploration of Outer Planets: Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 conducted flybys of Jupiter and Saturn.
- Voyager 2 was then directed to continue its mission to Uranus and Neptune, becoming the only spacecraft to visit these distant ice giant planets.
- Interstellar Mission: After completing their primary planetary missions, both spacecraft continued to travel outward from the solar system into interstellar space.
- Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause (the boundary between the solar system and interstellar space) in 2012, becoming the first human-made object to enter interstellar space.
- Discoveries: The Voyager missions provided significant scientific discoveries, including detailed images and data on the planets’ atmospheres, magnetic fields, and moons.
- Voyager 1 discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io and the intricate ring structure around Saturn.
- Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 discovered three new moons of Jupiter: Thebe, Metis and Adrastea.
- Longevity: The spacecraft have been operational for decades, both spacecraft are still functional making them some of the most enduring and successful space missions in history.
About NASA:
|
Post Views: 182
