Context
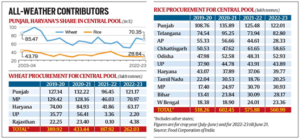
Punjab and Haryana is contributing to India’s food security, especially post the Green Revolution which is helping India’s concerns of low monsoon this year due to better irrigation facilities.- During the last two-years, the combined share of Punjab and Haryana in procurement declined to 50-51%, which has gone up in the last two years to 70-74%, reinforcing their status as reliable, “all-weather” contributors to national food security.
- As, the upcoming year is estimated to be an EL Nino year with delayed monsoon onset, the agriculture and Kharif crops are estimated to be impacted in India.
- The immediate impact of a subnormal monsoon would be on the kharif crops, the sowings of which have barely taken off.
- Moreover, if El Niño is going to get stronger, the impact could extend to the rabi (winter-spring) crops.
- These, particularly wheat, are grown using groundwater and dam reservoirs that are recharged/refilled during the monsoon. A subnormal monsoon can, in other words, hit both rice and wheat production.
- India is dependent on Rice and Wheat for its most of the food grain consumption and these weather events led to a sense of insecurity regarding food production and consumption.
- Punjab alone cultivated paddy (rice with husk) on 67 lakh hectares (lh) in 2022-23, including 4.94 lh under basmati varieties.
- The Punjab government is supplying eight hours of uninterrupted free power daily to run these tube-wells during the four-month paddy season (from transplanting to harvesting), starting June 10.
- Punjab — known as the ‘Granary of India’ — produces 20 per cent and nine per cent of India’s wheat and rice respectively.
- At the international level, this represents three per cent of the global production of these crops.
- The state is responsible for two per cent of the world’s cotton and wheat production and one per cent of the world’s rice production.
- The higher yield is possibly because of the Green Revolution, a period when Indian agriculture was converted into an industrial system.
- Modern methods and technology — including high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds, tractors, irrigation facilities, pesticides and fertilisers — were adopted.
 Food Security act, 2013:
Salient features:
Food Security act, 2013:
Salient features:
- Foodgrains are distributed at subsidized rates.
- Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Food Security Allowance.
- Transparency provisions are made available to avoid loop holes.
Food Security Programs in India:
|
- Significance of Act:
- To boost the Agriculture sector.
- Aids the Government to Regulate the Prices.
- Enhance reduction in poverty.
- Access to nutritious food.
- Also important for global security and national stability.
Post Views: 178
