Context
The Department of Space (DoS) has told the Parliamentary Committee of Science and Technology that the Navigation with Indian Constellation or (NavIC) is going to be integrated into Aadhaar enrolment devices.Navigation with Indian Constellation or (NavIC):
|
About the merger:
- Need: Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to Global Positioning system (GPS).
- The DoS has conducted successful field trials and is providing technical expertise for the finalisation of procurement specifications for the devices.
- Overall, the integration of NavIC into Aadhaar enrolment devices will enhance navigation accuracy and provide better disaster management capabilities.
- Significance:
- NavIC’s integration will enhance the accuracy and reliability of these devices.
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has been created, with the mandate of providing a Unique Identity (Aadhaar) to all Indian residents.
- The UIDAI provides online authentication using demographic and biometric data.
- Aadhaar authentication is the process involves Aadhaar Number, along with other attributes, including biometrics, is submitted online to the Aadhaar system for its verification on the basis of information or data or documents available with it.
- During the authentication transaction, the resident’s record is first selected using the Aadhaar Number and then the demographic/biometric inputs are matched against the stored data which was provided by the resident during enrolment/update process.
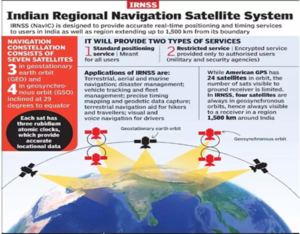
- NavIC offers two services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and;
- Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- These two services are provided in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S band (2498.028 MHz).
- NavIC coverage area includes India and a region up to 1,500 km beyond the Indian boundary.
- Newer satellites will have an additional band called L1 that will be compatible with civilian use.
- The National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) was already utilising NavIC as an alert dissemination system for major natural disasters like landslips, earthquakes, floods, and avalanches.
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information System (INCOIS) relies on NavIC to broadcast cyclones, high waves, and tsunamis alert messages to fishermen venturing into the deep sea.
 Organizations working with NavIC data:
Organizations working with NavIC data:
- NavIC standards were set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Telecom Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI), Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC), Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), and Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM), International Electrotechnical Committee (IEC), and International Standards Organisation (ISO).
- Threat to data security and sovereignty: System like GPS and GLONASS are operated by defence agencies of the respective nations.

Post Views: 206
