Context:
Indian Council of Medical Research’s National Institute of Virology (ICMR-NIV) has found evidence of the Nipah virus circulation in the bat population across nine states and one Union Territory.
About Nipah Virus:
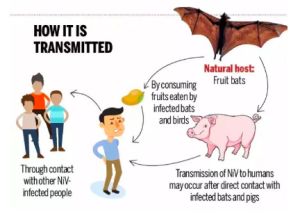
- The first outbreaks of the Nipah virus among humans was reported from Malaysia (1998) and Singapore (1999).

- It belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae, genus Henipavirus.
- Fatality Rate: The WHO estimates that between 40% and 75% of cases can result in death.
- Spread:
- It is a zoonotic virus, transmitted from animals to humans.
- Reservoir: The fruit bat, also known as the flying fox, serves as the animal host reservoir for the virus.
- Fruit bats transmit the virus to other animals such as pigs, dogs, cats, goats, horses, and sheep.
- Humans can get infected through direct contact with these infected animals or by consuming food contaminated with their saliva or urine.
- Symptoms: Fever, headache, drowsiness, disorientation, mental confusion, coma, potential death.
- Preventive Measures:
- Avoid physical contact with an infected person.
- Wash hands after caring for an infected person.
- Stay away from consuming raw date palm sap or toddy.
- Discard fruits with signs of bat bites.
- Treatments: No specific treatment for Nipah Virus, primary treatment is intensive supportive care.
Post Views: 172
